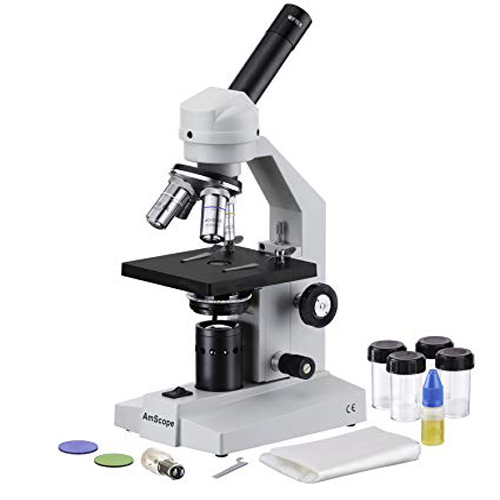
Equipment and Machinery
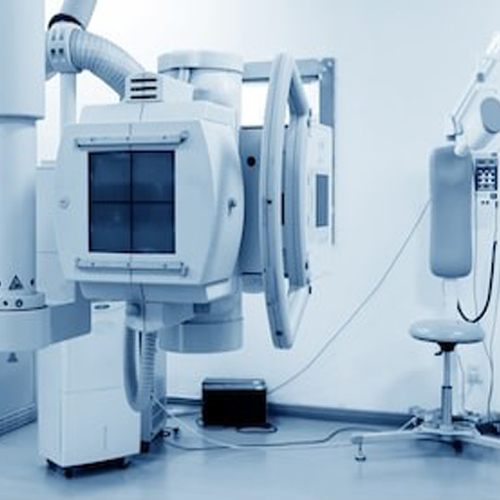
X-Ray Machine
An X-ray generator is a device that produces X-rays. Together with an X-ray detector, it is commonly used in a variety of applications including medicine, fluorescence, electronic assembly inspection, and measurement of material thickness in manufacturing operations. In medical applications, X-ray generators are used by radiographers to acquire x-ray images of the internal structures (e.g., bones) of living organisms, and also in sterilization.
In medical imaging applications, an x-ray machine has a control console that is used by a radiologic technologist to select x-ray attributes suitable for the specific exam, a power supply that creates and produces the desired kVp (peak kilovoltage), mA (milliamperes, sometimes referred to as mAs which is actually mA multiplied by the desired exposure length) for the x-ray tube, and the x-ray tube itself.
Specifications and uses:
An X-ray imaging system consists of a generator control console where the operator selects desired techniques to obtain a quality readable image(kVp, mA and exposure time), an x-ray generator which controls the x-ray tube current, x-ray tube kilovoltage and x-ray emitting exposure time, an X-ray tube that converts the kilovoltage and mA into actual x-rays and an image detection system which can be either a film (analog technology) or a digital capture system and a PACS.